| 1.4.1 用空间向量研究直线、平面的位置关系 题目答案及解析
稿件来源:高途
| 1.4.1 用空间向量研究直线、平面的位置关系题目答案及解析如下,仅供参考!
选择性必修一
第一章 空间向量与立体几何
1.4 空间向量的应用
1.4.1 用空间向量研究直线、平面的位置关系
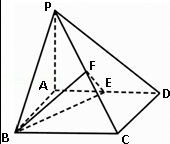
如图,四边形$ABCD$是矩形,$PA\perp$平面$ABCD$,$AP=AB=2$,$BC=2\sqrt{2}$,$E$,$F$分别是$AD$,$PC$的中点.建立适当的空间坐标系,利用空间向量详解以下问题:
$(1)$证明:$PC\perp$平面$BEF$;
$(2)$求平面$BEF$与平面$BAP$夹角的大小.
$(1)$证明见解析;
$(2)$$45^\\circ$
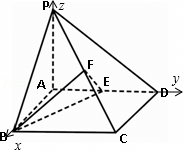
"]]$(1)$证明:如图,以$A$为坐标原点,$AB$,$AD$,$AP$所在直线分别为$x$,$y$,$z$轴建立空间直角坐标系.
$\because AP=AB=2,BC=AD=2\sqrt{2}$,四边形$ABCD$是矩形.
$\therefore A$,$B$,$C$,$D$,$P$的坐标为$A(0$,$0$,$0)$,$B(2$,$0$,$0)$,$C(2,2\sqrt{2},0)D(0,2\sqrt{2},0),P(0,0,2)$,
又$E$,$F$分别是$AD$,$PC$的中点,
$\therefore E(0,\sqrt{2},0),F(1,\sqrt{2},1)$,
$\therefore \overrightarrow{PC}=(2,2\sqrt{2},-2),\overrightarrow{BF}=(-1,\sqrt{2},1),\overrightarrow{EF}=(1,0,1)$,
$\therefore \overrightarrow{PC}\cdot \overrightarrow{BF}=-2+4-2=0,\overrightarrow{PC}\cdot \overrightarrow{EF}=2+0-2=0$,
$\therefore \overrightarrow{PC}\perp \overrightarrow{BF},\overrightarrow{PC}\perp \overrightarrow{EF}$,
又$\because BF\cap EF=F$,
$\therefore PC\perp$平面$BEF$
$(2)$解:由$(1)$知平面$BEF$的法向量$\overrightarrow{n_1}=\overrightarrow{PC}=(2,2\sqrt{2},-2)$,
平面$BAP$的法向量$\overrightarrow{n_2}=\overrightarrow{AD}=(0,2\sqrt{2},0)$,
$\therefore \overrightarrow{n_1}\cdot \overrightarrow{n_2}=8$
设平面$BEF$与平面$BAP$的夹角为$\theta$,
则$\cos \theta =\cos \lt \overrightarrow{n_1},\overrightarrow{n_2}\gt =\dfrac{\overrightarrow{n_1}\cdot \overrightarrow{n_2}}{\vert \overrightarrow{n_1}\vert \vert \overrightarrow{n_2}\vert }=\dfrac{8}{4\times 2\sqrt{2}}=\dfrac{\sqrt{2}}{2}$,
$\therefore \theta =45^\circ$,
$\therefore $平面$BEF$与平面$BAP$的夹角为$45^\circ$
| 1.4.1 用空间向量研究直线、平面的位置关系题目答案及解析(完整版)
